Insulation Resistance (IR) Values – Index
1. IR Values For Electrical Apparatus & Systems
2. IR Value for Transformer
3. IR Value for Tap Changer
4. IR Value for Electric motor
5. IR Value for Electrical cable and wiring
6. IR Value for Transmission / Distribution Line
7. IR Value for Panel Bus
8. IR Value for Substation Equipment
9. IR Value for Domestic /Industrial Wiring
0. Required Precautions
2. IR Value for Transformer
3. IR Value for Tap Changer
4. IR Value for Electric motor
5. IR Value for Electrical cable and wiring
6. IR Value for Transmission / Distribution Line
7. IR Value for Panel Bus
8. IR Value for Substation Equipment
9. IR Value for Domestic /Industrial Wiring
0. Required Precautions
1. IR Values For Electrical Apparatus & Systems
(PEARL Standard / NETA MTS-1997 Table 10.1)
| Max.Voltage Rating Of Equipment | Megger Size | Min.IR Value |
| 250 Volts | 500 Volts | 25 MΩ |
| 600 Volts | 1,000 Volts | 100 MΩ |
| 5 KV | 2,500 Volts | 1,000 MΩ |
| 8 KV | 2,500 Volts | 2,000 MΩ |
| 15 KV | 2,500 Volts | 5,000 MΩ |
| 25 KV | 5,000 Volts | 20,000 MΩ |
| 35 KV | 15,000 Volts | 100,000 MΩ |
| 46 KV | 15,000 Volts | 100,000 MΩ |
| 69 KV | 15,000 Volts | 100,000 MΩ |
One Meg ohm Rule for IR Value for Equipment
Based upon equipment rating:
< 1K V = 1 MΩ minimum
>1KV = 1 MΩ /1KV
>1KV = 1 MΩ /1KV
As per IE Rules-1956
At a pressure of 1000 V applied between each live conductor and earth for a period of one minute the insulation resistance of HV installations shall be at least 1 Mega ohm or as specified by the Bureau of Indian Standards.
Medium and Low Voltage Installations- At a pressure of 500 V applied between each live conductor and earth for a period of one minute, the insulation resistance of medium and low voltage installations shall be at least 1 Mega ohm or as specified by the Bureau of Indian Standards] from time to time.
As per CBIP specifications the acceptable values are 2 Mega ohms per KV
2. IR Value for Transformer
Insulation resistance tests are made to determine insulation resistance from individual windings to ground or between individual windings. Insulation resistance tests are commonly measured directly in megohms or may be calculated from measurements of applied voltage and leakage current.
The recommended practice in measuring insulation resistance is to always ground the tank (and the core). Short circuit each winding of the transformer at the bushing terminals. Resistance measurements are then made between each winding and all other windings grounded.
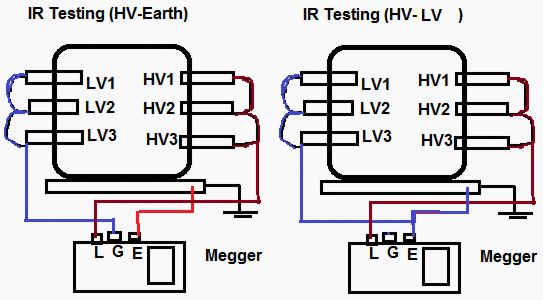 |
Insulation resistance testing: HV - Earth and HV - LV
|
Transformer windings are never left floating for insulation resistance measurements. Solidly grounded winding must have the ground removed in order to measure the insulation resistance of the winding grounded. If the ground cannot be removed, as in the case of some windings with solidly grounded neutrals, the insulation resistance of the winding cannot be measured. Treat it as part of the grounded section of the circuit.
We need to test winding to winding and winding to ground ( E ).For three phase transformers, We need to test winding ( L1,L2,L3 ) with substitute Earthing for Delta transformer or winding ( L1,L2,L3 ) with earthing ( E ) and neutral ( N ) for wye transformers.
| IR Value for Transformer (Ref: A Guide to Transformer Maintenance by. JJ. Kelly. S.D Myer) | |
| Transformer | Formula |
| 1 Phase Transformer | IR Value (MΩ) = C X E / (√KVA) |
| 3 Phase Transformer (Star) | IR Value (MΩ) = C X E (P-n) / (√KVA) |
| 3 Phase Transformer (Delta) | IR Value (MΩ) = C X E (P-P) / (√KVA) |
| Where C= 1.5 for Oil filled T/C with Oil Tank, 30 for Oil filled T/C without Oil Tank or Dry Type T/C. | |
Temperature correction Factor (Base 20°C):
| Temperature correction Factor | ||
| OC | OF | Correction Factor |
| 0 | 32 | 0.25 |
| 5 | 41 | 0.36 |
| 10 | 50 | 0.50 |
| 15 | 59 | 0.720 |
| 20 | 68 | 1.00 |
| 30 | 86 | 1.98 |
| 40 | 104 | 3.95 |
| 50 | 122 | 7.85 |
Example: For 1600KVA, 20KV/400V,Three Phase Transformer
- IR Value at HV Side= (1.5 x 20000) / √ 1600 =16000 / 40 = 750 MΩ at 200C
- IR Value at LV Side = (1.5 x 400 ) / √ 1600= 320 / 40 = 15 MΩ at 200C
- IR Value at 300C =15X1.98= 29.7 MΩ
Insulation Resistance of Transformer Coil
| Transformer Coil Voltage | Megger Size | Min.IR Value Liquid Filled T/C | Min.IR Value Dry Type T/C |
| 0 – 600 V | 1KV | 100 MΩ | 500 MΩ |
| 600 V To 5KV | 2.5KV | 1,000 MΩ | 5,000 MΩ |
| 5KV To 15KV | 5KV | 5,000 MΩ | 25,000 MΩ |
| 15KV To 69KV | 5KV | 10,000 MΩ | 50,000 MΩ |
IR Value of Transformers
| Voltage | Test Voltage (DC) LV side | Test Voltage (DC) HV side | Min IR Value |
| 415V | 500V | 2.5KV | 100MΩ |
| Up to 6.6KV | 500V | 2.5KV | 200MΩ |
| 6.6KV to 11KV | 500V | 2.5KV | 400MΩ |
| 11KV to 33KV | 1000V | 5KV | 500MΩ |
| 33KV to 66KV | 1000V | 5KV | 600MΩ |
| 66KV to 132KV | 1000V | 5KV | 600MΩ |
| 132KV to 220KV | 1000V | 5KV | 650MΩ |
Steps for measuring the IR of Transformer:
- Shut down the transformer and disconnect the jumpers and lightning arrestors.
- Discharge the winding capacitance.
- Thoroughly clean all bushings
- Short circuit the windings.
- Guard the terminals to eliminate surface leakage over terminal bushings.
- Record the temperature.
- Connect the test leads (avoid joints).
- Apply the test voltage and note the reading. The IR. Value at 60 seconds after application of the test voltage is referred to as the Insulation Resistance of the transformer at the test temperature.
- The transformer Neutral bushing is to be disconnected from earth during the test.
- All LV surge diverter earth connections are to be disconnected during the test.
- Due to the inductive characteristics of transformers, the insulation resistance reading shall not be taken until the test current stabilizes.
- Avoid meggering when the transformer is under vacuum.
Test Connections of Transformer for IR Test (Not Less than 200 MΩ)
Two winding transformer
1. (HV + LV) – GND
2. HV – (LV + GND)
3. LV – (HV + GND)
1. (HV + LV) – GND
2. HV – (LV + GND)
3. LV – (HV + GND)
Three winding transformer
1. HV – (LV + TV + GND)
2. LV – (HV + TV + GND)
3. (HV + LV + TV) – GND
4. TV – (HV + LV + GND)
1. HV – (LV + TV + GND)
2. LV – (HV + TV + GND)
3. (HV + LV + TV) – GND
4. TV – (HV + LV + GND)
Auto transformer (two windings)
1. (HV + LV) – GND
1. (HV + LV) – GND
Auto Transformer (three winding)
1. (HV + LV) – (TV + GND)
2. (HV + LV + TV) – GND
3. TV – (HV + LV + GND)
1. (HV + LV) – (TV + GND)
2. (HV + LV + TV) – GND
3. TV – (HV + LV + GND)
For any installation, the insulation resistance measured shall not be less than:
- HV – Earth 200 M Ω
- LV – Earth 100 M Ω
- HV – LV 200 M Ω
Factors affecting on IR value of Transformer
The IR value of transformers are influenced by
- Surface condition of the terminal bushing
- Quality of oil
- Quality of winding insulation
- Temperature of oil
- Duration of application and value of test voltage
3. IR Value for Tap Changer
- IR between HV and LV as well as windings to earth.
- Minimum IR value for Tap changer is 1000 ohm per volt service voltage
4. IR Value for Electric motor
For electric motor, we used a insulation tester to measure the resistance of motor winding with earthing (E).
- For rated voltage below 1KV, measured with a 500VDC Megger.
- For rated voltage above 1KV, measured with a 1000VDC Megger.
- In accordance with IEEE 43, clause 9.3, the following formula should be applied.
- Min IR Value (For Rotating Machine) =(Rated voltage (v) /1000) + 1
 |
| Insulation resistance (IR) value for electric motor |
| As per IEEE 43 Standard 1974, 2000 | |
| IR Value in MΩ | |
| IR (Min) = kV+1 | For most windings made before about 1970, all field windings, and others not described below |
| IR (Min) = 100 MΩ | For most dc armature and ac windings built after about 1970 (form wound coils) |
| IR (Min) = 5 MΩ | For most machines with random -wound stator coils and form-wound coils rated below 1kV |
Example-1: For 11KV, Three Phase Motor.
- IR Value =11+1=12 MΩ but as per IEEE43 It should be 100 MΩ
- Example-2: For 415V,Three Phase Motor
- IR Value =0.415+1=1.41 MΩ but as per IEEE43 It should be 5 MΩ.
- As per IS 732 Min IR Value of Motor=(20XVoltage(p-p/(1000+2XKW)
IR Value of Motor as per NETA ATS 2007. Section 7.15.1
| Motor Name Plate (V) | Test Voltage | Min IR Value |
| 250V | 500V DC | 25 MΩ |
| 600V | 1000V DC | 100MΩ |
| 1000V | 1000V DC | 100MΩ |
| 2500V | 1000V DC | 500MΩ |
| 5000V | 2500V DC | 1000MΩ |
| 8000V | 2500V DC | 2000MΩ |
| 15000V | 2500V DC | 5000MΩ |
| 25000V | 5000V DC | 20000MΩ |
| 34500V | 15000V DC | 100000MΩ |
IR Value of Submersible Motor:
| IR Value of Submersible Motor | |
| Motor Out off Well (Without Cable) | IR Value |
| New Motor | 20 MΩ |
| A used motor which can be reinstalled | 10 MΩ |
| Motor Installed in Well (With Cable) | |
| New Motor | 2 MΩ |
| A used motor which can be reinstalled | 0.5 MΩ |
5. IR Value for Electrical cable and wiring
For insulation testing, we need to disconnect from panel or equipment and keep them isolated from power supply. The wiring and cables need to test for each other ( phase to phase ) with a ground ( E ) cable. The Insulated Power Cable Engineers Association (IPCEA) provides the formula to determine minimum insulation resistance values.
R = K x Log 10 (D/d)
R = IR Value in MΩs per 1000 feet (305 meters) of cable.
K = Insulation material constant.( Varnished Cambric=2460, Thermoplastic Polyethlene=50000,Composite Polyethylene=30000)
D = Outside diameter of conductor insulation for single conductor wire and cable ( D = d + 2c + 2b diameter of single conductor cable )
d – Diameter of conductor
c – Thickness of conductor insulation
b – Thickness of jacket insulation
K = Insulation material constant.( Varnished Cambric=2460, Thermoplastic Polyethlene=50000,Composite Polyethylene=30000)
D = Outside diameter of conductor insulation for single conductor wire and cable ( D = d + 2c + 2b diameter of single conductor cable )
d – Diameter of conductor
c – Thickness of conductor insulation
b – Thickness of jacket insulation
HV test on new XLPE cable (As per ETSA Standard)
| Application | Test Voltage | Min IR Value |
| New cables – Sheath | 1KV DC | 100 MΩ |
| New cables – Insulation | 10KV DC | 1000 MΩ |
| After repairs – Sheath | 1KV DC | 10 MΩ |
| After repairs – Insulation | 5KV DC | 1000MΩ |
11kV and 33kV Cables between Cores and Earth (As per ETSA Standard)
| Application | Test Voltage | Min IR Value |
| 11KV New cables – Sheath | 5KV DC | 1000 MΩ |
| 11KV After repairs – Sheath | 5KV DC | 100 MΩ |
| 33KV no TF’s connected | 5KV DC | 1000 MΩ |
| 33KV with TF’s connected. | 5KV DC | 15MΩ |
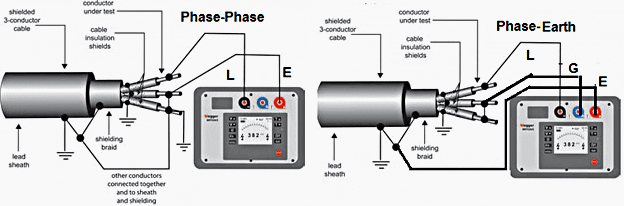 |
| 11kV and 33kV Cables between Cores and Earth |
IR Value Measurement (Conductors to conductor (Cross Insulation))
- The first conductor for which cross insulation is being measured shall be connected to Line terminal of the megger. The remaining conductors looped together (with the help of crocodile clips) i. e. Conductor 2 and onwards, are connected to Earth terminal of megger. Conductors at the other end are left free.
- Now rotate the handle of megger or press push button of megger. The reading of meter will show the cross Insulation between conductor 1 and rest of the conductors. Insulation reading shall be recorded.
- Now connect next conductor to Line terminal of the megger & connect the remaining conductors to earth terminal of the megger and take measurements.
IR Value Measurement (Conductor to Earth Insulation)
- Connect conductor under test to the Line terminal of the megger.
- Connect earth terminal of the megger to the earth.
- Rotate the handle of megger or press push button of megger. The reading of meter will show the insulation resistance of the conductors. Insulation reading shall be recorded after applying the test voltage for about a minute till a steady reading is obtained.
IR Value Measurements:
- If during periodical testing, insulation resistance of cable is found between 5 and 1 MΩ /km at buried temperature, the subject cable should be programmed for replacement.
- If insulation resistance of the cable is found between 1000 and 100 KΩ /km, at buried temperature, the subject cable should be replaced urgently within a year.
- If the insulation resistance of the cable is found less than 100 kilo ohm/km., the subject cable must be replaced immediately on emergency basis.
6. IR Value for Transmission / Distribution Line
| Equipment | Megger Size | Min IR Value |
| S/S .Equipments | 5 KV | 5000MΩ |
| EHVLines. | 5 KV | 10MΩ |
| H.T. Lines. | 1 KV | 5MΩ |
| LT / Service Lines. | 0.5 KV | 5MΩ |
7. IR Value for Panel Bus
IR Value for Panel = 2 x KV rating of the panel.
Example, for a 5 KV panel, the minimum insulation is 2 x 5 = 10 MΩ.
Example, for a 5 KV panel, the minimum insulation is 2 x 5 = 10 MΩ.
8. IR Value for Substation Equipment
Generally meggering Values of Substation Equipments are.
| Typical IR Value of S/S Equipments | |||
| Equipment | Megger Size | IR Value(Min) | |
| Circuit Breaker | (Phase-Earth) | 5KV,10 KV | 1000 MΩ |
| (Phase-Phase) | 5KV,10 KV | 1000 MΩ | |
Control Circuit
| 0.5KV | 50 MΩ | |
CT/PT
| (Pri-Earth) | 5KV,10 KV |
1000 MΩ
|
| (Sec-Phase) | 5KV,10 KV | 50 MΩ | |
| Control Circuit |
0.5KV
| 50 MΩ | |
| Isolator | (Phase-Earth) | 5KV,10 KV | 1000 MΩ |
| (Phase-Phase) | 5KV,10 KV | 1000 MΩ | |
| Control Circuit | 0.5KV | 50 MΩ | |
| L.A | (Phase-Earth) | 5KV,10 KV | 1000 MΩ |
| Electrical Motor | (Phase-Earth) | 0.5KV | 50 MΩ |
| LT Switchgear | (Phase-Earth) | 0.5KV | 100 MΩ |
| LT Transformer | (Phase-Earth) | 0.5KV | 100 MΩ |
| IR Value of S/S Equipments As per DEP Standard | |||
| Equipment | Meggering | IR Value at Commissioning Time (MΩ) | IR Value at Maintenance Time |
| Switchgear | HV Bus | 200 MΩ | 100 MΩ |
| LV Bus | 20 MΩ | 10 MΩ | |
| LV wiring | 5 MΩ | 0.5 MΩ | |
| Cable(min 100 Meter) | HV & LV | (10XKV) / KM | (KV) / KM |
| Motor & Generator | Phase-Earth | 10(KV+1) | 2(KV+1) |
| Transformer Oil immersed | HV & LV | 75 MΩ | 30 MΩ |
| Transformer Dry Type | HV | 100 MΩ | 25 MΩ |
| LV | 10 MΩ | 2 MΩ | |
| Fixed Equipments/Tools | Phase-Earth | 5KΩ / Volt | 1KΩ / Volt |
| Movable Equipments | Phase-Earth | 5 MΩ | 1MΩ |
| Distribution Equipments | Phase-Earth | 5 MΩ | 1MΩ |
| Circuit Breaker | Main Circuit | 2 MΩ / KV | - |
| Control Circuit | 5MΩ | - | |
| Relay | D.C Circuit-Earth | 40MΩ | - |
| LT Circuit-Earth | 50MΩ | - | |
| LT-D.C Circuit | 40MΩ | - | |
| LT-LT | 70MΩ | - | |
9. IR Value for Domestic /Industrial Wiring
A low resistance between phase and neutral conductors, or from live conductors to earth, will result in a leakage current. This cause deterioration of the insulation, as well as involving a waste of energy which would increase the running costs of the installation.
The resistance between Phase-Phase-Neutral-Earth must never be less than 0.5 M Ohms for the usual supply voltages.
In addition to the leakage current due to insulation resistance, there is a further current leakage in the reactance of the insulation, because it acts as the dielectric of a capacitor. This current dissipates no energy and is not harmful, but we wish to measure the resistance of the insulation, so DC Voltage is used to prevent reactance from being included in the measurement.
1 Phase Wiring
>The IR test between Phase-Natural to earth must be carried out on the complete installation with the main switch off, with phase and neutral connected together, with lamps and other equipment disconnected, but with fuses in, circuit breakers closed and all circuit switches closed.
Where two-way switching is wired, only one of the two stripper wires will be tested. To test the other, both two-way switches should be operated and the system retested. If desired, the installation can be tested as a whole, when a value of at least 0.5 M Ohms should be achieved.
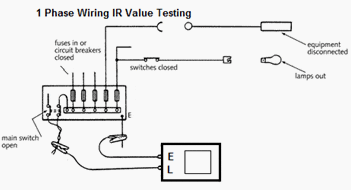 |
1 Phase Wiring
|
3 Phase Wiring
In the case of a very large installation where there are many earth paths in parallel, the reading would be expected to be lower. If this happens, the installation should be subdivided and retested, when each part must meet the minimum requirement.
 |
3 Phase Wiring
|
The IR tests must be carried out between Phase-Phase-Neutral-Earth with a minimum acceptable value for each test of 0.5 M Ohms.
| IR Testing for Low voltage | ||
| Circuit voltage | Test voltage | IR Value(Min) |
| Extra Low Voltage | 250V DC | 0.25MΩ |
| Up to 500 V except for above | 500 V DC | 0.5MΩ |
| 500 V To 1KV | 1000 V DC | 1.0MΩ |
Min IR Value = 50 MΩ / No of Electrical outlet. (All Electrical Points with fitting & Plugs)
Min IR Value = 100 MΩ / No of Electrical outlet. (All Electrical Points without fitting & Plugs).
Min IR Value = 100 MΩ / No of Electrical outlet. (All Electrical Points without fitting & Plugs).
Required Precautions
Electronic equipment like electronic fluorescent starter switches, touch switches, dimmer switches, power controllers, delay timers could be damaged by the application of the high test voltage should be disconnected.
Capacitors and indicator or pilot lamps must be disconnected or an inaccurate test reading will result.
Where any equipment is disconnected for testing purposes, it must be subjected to its own insulation test, using a voltage which is not likely to result in damage. The result must conform with that specified in the British Standard concerned, or be at least 0.5 M Ohms if there is no Standard.
I can see that you are an expert at your field! I am launching a website soon, and your information will be very useful for me.. Thanks for all your help and wishing you all the success in your business. attic insulation removal and replacement
ReplyDeleteI have a question, a few days ago I used the Megger equipment to do the insulation tests on transformers and on three transformers specifically I failed the HV + LV-G test, I wanted to see if anyone has had this problem with this specific test
ReplyDelete